These arrays, which can contain 4 - 128 drives, also contain rebuild areas that are used to maintain redundancy after a drive fails. As a result, the distributed configuration dramatically reduces rebuild times and decreases the exposure volumes have to the extra load of recovering redundancy.
Distributed RAID arrays solve these problems because rebuild areas are distributed across all the drives in the array. The rebuild write workload is spread across all the drives rather just the single spare drive which results in faster rebuilds on an array. Distributed array configurations may contain between 4 - 128 drives. Distributed arrays remove the need for separate drives that are idle until a failure occurs. Instead of allocating one or more drives as spares, the spare capacity is distributed over specific rebuild areas across all the member drives. Data can be copied faster to the rebuild area and redundancy is restored much more rapidly. Additionally, as the rebuild progresses, the performance of the pool is more uniform because all of the available drives are used for every volume extent. After the failed drive is replaced, data is copied back to the drive from the distributed spare capacity. Unlike "hot spares" drives, read/write requests are processed on other parts of the drive that are not being used as rebuild areas. The number of rebuild areas is based on the width of the array. The size of the rebuild area determines how many times the distributed array can recover failed drives without risking becoming degraded. For example, a distributed array that uses RAID 6 drives can handle two concurrent failures. After the failed drives have been rebuilt, the array can tolerate another two drive failures. If all of the rebuild areas are used to recover data, the array becomes degraded on the next drive failure.
Supported RAID levels
The system supports the following RAID levels for distributed arrays.
- Distributed RAID 5 arrays stripe data over the member drives with one parity strip on every stripe. These distributed arrays can support 4 - 128 drives. RAID 5 distributed arrays can tolerate the failure of one member drive.
- Distributed RAID 6 arrays stripe data over the member drives with two parity strips on every stripe. These distributed arrays can support 6 - 128 drives. A RAID 6 distributed array can tolerate any two concurrent member drive failures.
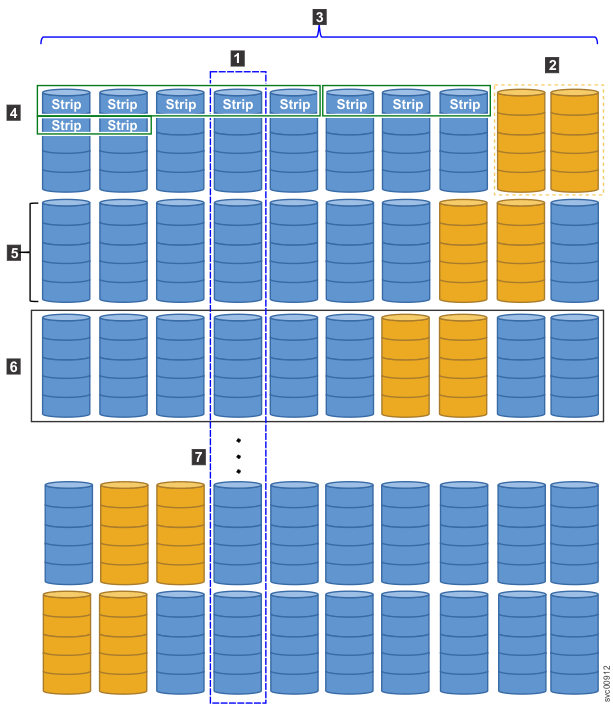
Example of a distributed array
- 1 An active drive
- 2 Rebuild areas, which distributed across all drives
- 3 Drive count, which includes all drives
- 4 Stripes of data (2 stripes are shown)
- 5 Stripe width
- 6 Pack, which equals the drive count that is multiplied by stripe width
- 7 Additional packs in the array (not shown)
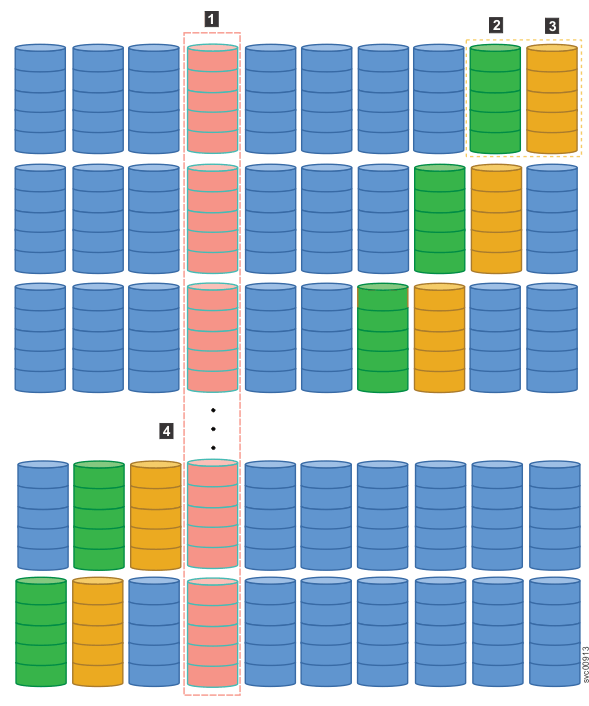
- 1 Failed drive
- 2 Rebuild areas, which are distributed across all drives
- 3 Remaining rebuild areas rotate across each remaining drive
- 4 Additional packs in the array (not shown)
Array width
The array width, which is also referred to as the drive count, indicates the total number of drives in a distributed array. This total includes the number of drives that are used for data capacity and parity, and the rebuild area that is used to recover data.
Rebuild area
The rebuild area is the disk capacity that is reserved within a distributed array to regenerate data after a drive failure; it provides no usable capacity. Unlike a nondistributed array, the rebuild area is distributed across all of the drives in the array. As data is rebuilt during the copyback process, the rebuild area contributes to the performance of the distributed array because all of the volumes perform I/O requests.
Stripe and stripe width
A stripe, which can also be referred to as a redundancy unit, is the smallest amount of data that can be addressed. For distributed arrays, the stripe size can be 128 or 256 KiB.
The stripe width indicates the number of stripes of data that can be written at one time when data is regenerated after a drive fails. This value is also referred to as the redundancy unit width. In Figure 1, the stripe width of the array is 5.
Drive class
To replace a failed member drive in the distributed array, the system can use another drive that has the same drive class as the failed drive. The system can also select a drive from a superior drive class. For example, two drive classes can contain drives of the same technology type but different data capacities. In this case, the superior drive class is the drive class that contains the higher capacity drives.
To display information about all of the drive classes that are available on the system, use the lsdriveclass command. Example output from the lsdriveclass command shows four drive classes on the system. Drive class 209 contains drives with a capacity of 278.9 GB; drive class 337 contains drives with a capacity of 558.4 GB. Although the drives have the same RPM speed, technology type, and block size, drive class 337 is considered to be superior to drive class 209.
Example output from the lsdriveclass command
id RPM capacity IO_group_id IO_group_name tech_type block_size candidate_count superior_count total_count 1 10000 418.7GB 0 io_grp0 sas_hdd 512 0 0 2 129 10000 278.9GB 0 io_grp0 sas_hdd 512 0 0 5 209 15000 278.9GB 2 io_grp2 sas_hdd 4096 2 5 2 337 15000 558.4GB 3 io_grp3 sas_hdd 4096 3 3 3
Slow write priority settings
When a redundant array is doing read/write I/O operations, the performance of the array is bound by the performance of the slowest member drive. If the SAS network is unstable or if too much work is being driven to the array when drives do internal ERP processes, performance to member drives can be far worse than usual. In this situation, arrays that offer redundancy can accept a short interruption to redundancy to avoid writing to, or reading from, the slow component. Writes that are mapped to a poorly performing drive are committed to the other copy or parity, and are then completed with good status (assuming no other failures). When the member drive recovers, the redundancy is restored by a background process of writing the strips that were marked out of sync while the member was slow.
This technique is governed by the setting of the slow_write_priority attribute of the distributed array, which defaults to latency when the array is created. When set to latency, the array is allowed to become out of sync in an attempt to smooth poor member performance. You can use the charray command to change the slow_write_priority attribute to redundancy. When set to redundancy, the array is not allowed to become out of sync. However, the array can avoid suffering read performance loss by returning reads to the slow component from redundant paths.
When the array uses latency mode or attempts to avoid reading a component that is in redundancy mode, the system evaluates the drive regularly to assess when it becomes a reliable part of the system again. If the drive never offers good performance or causes too many performance failures in the array, the system fails the hardware to prevent ongoing exposure to the poor-performing drive. The system fails the hardware only if it cannot detect another explanation for the bad performance from the drive.
Distributed drive replacement
If the fault LED light on a drive is lit, the drive is marked as failed and is no longer used in the distributed array. When the system detects that a failed drive was replaced, it automatically removes the failed hardware from the array configuration. If the new drive is suitable (for example, in the same drive class), the system begins a copyback operation to make a rebuild area available in the distributed array.