You can use more than four fabric ports per Lenovo Storage V7000node canister to improve peak load I/O performance, but careful planning is needed.
A fabric port is a Fibre Channel port or a Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) port. If you use more than four fabric ports per node, you must either use the localfcportmask and partnerfcportmask commands or be careful with your fabric zoning configuration.
If a node canister receives more than 16 logins from another node, then it causes node error 860.
- Zone the SAN fabric to reduce the number of paths between the nodes.
- Apply a local Fibre Channel port mask (if the nodes are within the same system) or partner Fibre Channel port mask (if the nodes are in different systems) to reduce the number of ports that are being used for node-to-node communication.
- Provide a combination of the two (zoning and port masks).
- For redundancy, use a minimum of two ports. If ports are being dedicated for different types of traffic, assign a minimum of two ports for each type of traffic.
- Within a system, up to 50% of the overall data that is transferred across the SAN is transmitted between the nodes. However, for read-intensive workloads, the figure is much less. Therefore, if ports are being dedicated for different types of traffic, assign between 1/4 and 1/2 of the overall ports for node-to-node communication within a system.
- For replication between systems, the connection between the systems is usually the bottleneck. Other than for redundancy, there is no point in having more SAN connections than there is bandwidth. For example, if two sites are connected with a 10 Gbps link, two 8 Gbps ports are sufficient. Systems usually are configured with two ports per node for replication traffic primarily for redundancy. For systems with larger numbers of nodes, it might be appropriate to have connections only from a subset of the nodes for replication to a remote system. The system automatically forwards replication traffic between local nodes so that all nodes can still participate in replication.
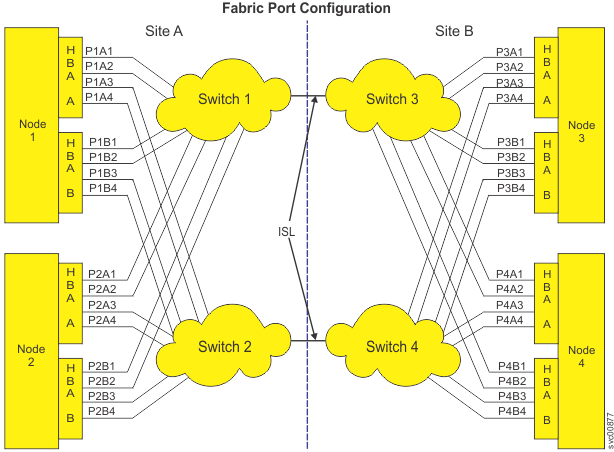
- Four nodes, where nodes 1 and 2 are in a system on site A. Nodes 3 and 4 are in a system on site B.
- Each site has 2 switches (switch 1 and 2 on site A; switch 3 and 4 on site B).
- Each node has 2 adapters (A and B).
- Each adapter has 4 ports where the port is named P nodeidadapteridportnumber. For example, port 3 on adapter B of node 4 is named P4B3.
Example 1: Zoning only
- Four ports are used for host, controller, and local node connections.
- Four ports are used for Global Mirror and Metro Mirror.
The following zones are required for two sites, A and B:
- Zone for storage controllers and local node connections (Fibre
Channel adapter HBA)
- Zone 1 - [ Lenovo Storage V7000 ports P1A1, P1A2, P2A1, P2A2 plus all storage controller ports in site A on switch 1]
- Zone 2 - [ Lenovo Storage V7000 ports P1A3, P1A4, P2A3, P2A4 plus all storage controller ports in site A on switch 2]
- Zones for host attachment (Fibre Channel adapter HBA A)
- The same ports on the first adapter are zoned to be visible to
hosts. It is recommended that each host is in a separate zone, and
a host with two ports that are connected to two fabrics have two zones,
one per fabric. The actual number of zones might be two multiplied
by the number of hosts. A host with four ports that are connected
to two fabrics should have four zones. In this case, the actual number
of zones might be four multiplied by the number of hosts. In the
four-port host case, the zones for one host might be:
- Zone 3 - [host port ,P1A1 and P2A1 for multipath failover] on switch 1
- Zone 4 - [host port ,P1A2 and P2A2 for multipath failover] on switch 1
- Zone 5 - [host port, P1A3 and P2A3 for multipath failover] on switch 2
- Zone 6 - [host port ,P1A4 and P2A4 for multipath failover] on switch 2
- The same ports on the first adapter are zoned to be visible to
hosts. It is recommended that each host is in a separate zone, and
a host with two ports that are connected to two fabrics have two zones,
one per fabric. The actual number of zones might be two multiplied
by the number of hosts. A host with four ports that are connected
to two fabrics should have four zones. In this case, the actual number
of zones might be four multiplied by the number of hosts. In the
four-port host case, the zones for one host might be:
- Zones for Global Mirror and Metro Mirror (Fibre Channel adapter HBA B only): To ensure Global Mirror and Metro Mirror use the second Fibre Channel adapter exclusively, it is required that each local or remote port pair has its own zone:
- Zone 7 - [P1B1,P3B1]
- Zone 8 - [P1B1,P3B2]
- Zone 9 - [P1B1,P4B1]
- Zone 10 - [P1B1,P4B2]
- Zone 11 - [P1B2,P3B1]
- Zone 12 - [P1B2,P3B2]
- Zone 13 - [P1B2,P4B1]
- Zone 14 - [P1B2,P4B2]
- Zone 15 - [P2B1,P3B1]
- Zone 16 - [P2B1,P3B2]
- Zone 17 - [P2B1,P4B1]
- Zone 18 - [P2B1,P4B2]
- Zone 18 - [P2B1,P4B2]
- Zone 19 - [P2B1,P4B2]
- Zone 20 - [P2B2,P3B2]
- Zone 21 - [P2B2,P4B1]
- Zone 22 - [P2B2,P4B2]
Zone sets for site B:
- Zone for storage controllers and local node connections (Fibre
Channel adapter HBA A):
- Zone 23 - [ Lenovo Storage V7000 ports P3A1, P3A2, P4A1, P4A2 plus all storage controller ports in site B on switch 3]
- Zone 24 - [ Lenovo Storage V7000 ports P3A3, P3A4, P4A3, P4A4 plus all storage controller ports in site B on switch 4]
- Zones for host attachment (Fibre Channel adapter HBA A)
- The same ports on the first adapter are zoned to be visible to
hosts. Only zones for one host are listed. It is recommended that
each host be in a separate zone. A host with two ports that are connected
to two fabrics has two zones, one per fabric. The actual number of
zones might be two multiplied by the number of hosts. A host with
four ports that are connected to two fabrics should have four zones.
In this case, the actual number of zones might be four multiplied
by the number of hosts. In the four-port host case, the zones for
one host might be:
- Zone 25 - [host ports ,P3A1 and P4A1 for multipath failover] on switch 3
- Zone 26 - [host ports ,P3A2 and P4A2 for multipath failover] on switch 3
- Zone 27 - [host ports, P3A3 and P4A3 for multipath failover] on switch 4
- Zone 28 - [host ports ,P3A4 and P4A4 for multipath failover] on switch 4
- The same ports on the first adapter are zoned to be visible to
hosts. Only zones for one host are listed. It is recommended that
each host be in a separate zone. A host with two ports that are connected
to two fabrics has two zones, one per fabric. The actual number of
zones might be two multiplied by the number of hosts. A host with
four ports that are connected to two fabrics should have four zones.
In this case, the actual number of zones might be four multiplied
by the number of hosts. In the four-port host case, the zones for
one host might be:
- Zones for Global Mirror and Metro Mirror (Fibre Channel adapter HBA B only):
To ensure Global Mirror and Metro Mirror use the second Fibre Channel adapter exclusively, it is required that each local or remote port pair has its own zone:
- Zone 29 - [P1B3,P3B3]
- Zone 30 - [P1B3,P3B4]
- Zone 31 - [P1B3,P4B3]
- Zone 32 - [P1B3,P4B4]
- Zone 33 - [P1B4,P3B3]
- Zone 34 - [P1B4,P3B4]
- Zone 35 - [P1B4,P4B3]
- Zone 36 - [P1B4,P4B4]
- Zone 37 - [P2B3,P3B3]
- Zone 38 - [P2B3,P3B4]
- Zone 39 - [P2B3,P4B3]
- Zone 40 - [P2B3,P4B4]
- Zone 41 - [P2B4,P3B3]
- Zone 42 - [P2B4,P3B4]
- Zone 43 - [P2B4,P4B3]
- Zone 44 - [P2B4,P4B4]
Example 2: Port masking only
Assuming the same configuration as in example 1, you can achieve the same result by using port masking rather than zoning.
For remote partnership communication, apply a mask limiting communication to ports B1, B2, B3, and B4 by applying a port mask of 11110000 to both systems by using the command chsystem -partnerfcportmask 11110000.
For local node-to-node communication, apply a mask limiting communication to ports A1, A2, A3, and A4 by applying a port mask of 00001111 to both systems by using the command chsystem -localfcportmask 00001111.
It is then possible to have a single zone that contains all the node ports, as the port masking ensures that the number of logins is no more than 16.
With this setup, zoning for host connectivity and storage connectivity does not need to take into account the rules about more than 16 logins.