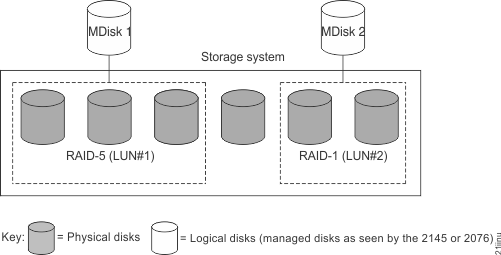
A managed disk (MDisk) is a logical unit of physical storage. MDisks are either arrays (RAID) from internal storage or volumes from external storage systems. MDisks are not visible to host systems.
An MDisk might consist of multiple physical disks that are presented as a single logical disk to the storage area network (SAN). An MDisk always provides usable blocks of physical storage to the system even if it does not have a one-to-one correspondence with a physical disk.
Each MDisk is divided into a number of extents, which are numbered, from 0, sequentially from the start to the end of the MDisk. The extent size is a property of pools. When an MDisk is added to a pool, the size of the extents that the MDisk is divided into depends on the attribute of the pool to which it has been added.
Access modes
- Unmanaged
- The MDisk is not used by the system.
- Managed
- The MDisk is assigned to a storage pool and provides extents that volumes can use.
- Image
- The MDisk is assigned directly to a volume with a one-to-one mapping of extents between the MDisk and the volume.
- Array
- The MDisk represents a set of drives in a RAID from internal storage.
| Status | Description |
| Online | The MDisk can be accessed by all online nodes. That is, all the nodes that are currently working members of the
system can access this MDisk. The MDisk is online when the following
conditions are met:
|
| Degraded paths | The MDisk is not accessible to one or more
nodes in the system. Degraded path status is most likely the result
of incorrect configuration of either the storage system or the Fibre Channel fabric.
However, hardware failures in the storage system, Fibre Channel fabric,
or node could also be a contributing factor to this state. To recover
from this state, follow these steps:
|
| Degraded ports | The MDisk has one or more 1220 errors in the event log. The 1220 error indicates that the remote Fibre Channel port has been excluded from the MDisk. This error might cause reduced performance on the storage system and usually indicates a hardware problem with the storage system. To fix this problem, you must resolve any hardware problems on the storage system and fix the 1220 errors in the event log. |
| Excluded | The MDisk has been excluded from use by the system after repeated access errors. Run the directed maintenance procedures to determine the problem. |
| Offline | The MDisk cannot be accessed by any of the online nodes. That is, all of the nodes that are currently working members of the system cannot access this MDisk. This state can be caused by a failure in the SAN, storage system, or one or more physical disks connected to the storage system. The MDisk is reported as offline if all paths to the disk fail. |
includemdisk mdiskname/idwhere mdiskname/id is the name or ID of your MDisk.
Extents
Each MDisk is divided into chunks of equal size called extents. Extents are a unit of mapping that provide the logical connection between MDisks and volume copies.
MDisk path
Each MDisk from external storage has an online path count, which is the number of nodes that have access to that MDisk; this represents a summary of the I/O path status between the system nodes and the storage device. The maximum path count is the maximum number of paths that have been detected by the system at any point in the past. If the current path count is not equal to the maximum path count, the MDisk might be degraded. That is, one or more nodes might not see the MDisk on the fabric.