The system supports all models of Compellent systems (storage controllers).
For the latest supported models, see the following Web sites:
For Lenovo Storage V3700 V2 and Lenovo Storage V3700 V2 XP: https://datacentersupport.lenovo.com/us/en/products/storage/lenovo-storage/v3700v2/6535
For Lenovo Storage V5030: https://datacentersupport.lenovo.com/us/en/products/storage/lenovo-storage/v5030/6536
Supported firmware levels for the Compellent system
The Compellent system must use a firmware level that is supported by the system. For specific firmware levels and the latest supported hardware, see the following Web sites:
For Lenovo Storage V3700 V2 and Lenovo Storage V3700 V2 XP: https://datacentersupport.lenovo.com/us/en/products/storage/lenovo-storage/v3700v2/6535
For Lenovo Storage V5030: https://datacentersupport.lenovo.com/us/en/products/storage/lenovo-storage/v5030/6536
Concurrent maintenance on the Compellent system
Concurrent maintenance is the capability to perform I/O operations to a Compellent system while simultaneously performing maintenance operations on it. You can perform nondisruptive maintenance procedures concurrently on the following components:
User interfaces on the Compellent system
The Compellent Storage Center GUI (graphical user interface) is used to manage the storage center. Compellent provides access to your Compellent system from any standard Internet browser or from any host computer via a local area network (LAN) or a wide area network (WAN).
Logical unit creation, deletion, and migration for Compellent systems
Before you create, delete, or migrate logical units, you must read the storage configuration guidelines that are specified in the Compellent documentation.
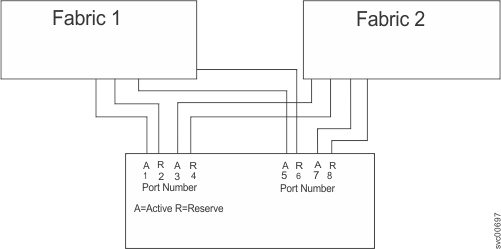
Cabling the Compellent system
Using the Compellent GUI to create storage pools
On the Compellent storage system, a storage pool is a collection of physical disks. In most implementations, all the disks are allocated to the assigned pool, and the data is automatically arranged into a tier of storage.
You can then select disks and create a new storage pool.
Using the Compellent GUI to create volumes
You can then select a storage pool, specify a size, and create a new volume.
Using the Compellent GUI to create servers
To assign storage to the system, you must create a server object that represents each storage node in the systemclustered system.
You can then select the host bus adapters, assign a name, specify an operating system, and create a new server.
When you create server objects for storage nodes, select as the operating system. After you create all your storage nodes as servers, consider creating a server cluster and adding all related nodes to it.
Using the Compellent GUI to map volumes to servers
You then can select the volume and perform the volume mapping.
Migrating volumes
You can use the standard migration procedure to migrate volumes from the Compellent system to the system.
Sharing the Compellent system between a host and the system
You can configure your environment so that other hosts can communicate with the Compellent system for storage requirements that fall outside of the system. You can also configure hosts that communicate directly with the system for storage to also communicate directly with the Compellent Storage Center for storage. Ensure that you carefully plan and have suitable documentation before you follow either of these scenarios.
Quorum disks on the Compellent system
The system can use logical units (LUs) that are exported by the Compellent system as quorum disks.
Advanced functions for the Compellent system
Compellent advanced functions are not supported by the system.