An active-active relationship is used to manage the synchronous replication of volume data between two sites. You must make the master volume accessible through either I/O group. The synchronizing process starts after change volumes are added to the active-active relationship.
When you work with active-active relationships, follow these guidelines
and requirements:
Active-active (HyperSwap®) relationship group states
Table 1 describes the active-active (HyperSwap®), relationship group states:| Management GUI icon1 | State | Description |
|---|---|---|
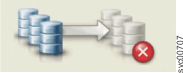 |
Inconsistent (stopped) | Both change volumes are not defined in the relationship. |
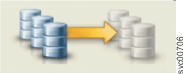 |
Inconsistent (copying) | The relationship is performing initial synchronization of data to the second copy. |
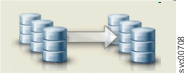 |
Consistent (stopped) | Either the relationship was created with -sync and both change volumes are not defined or a change volume was force-deleted after the relationship synchronized. |
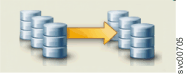 |
Consistent (copying) | The two copies are different, but resynchronization occurs when it can. During the copy, the status field is online. When the system is unable to copy, the status field shows what is preventing the copy. |
 |
Consistent (synchronized) | The two copies both contain all completed host-write operations. The high availability failover and read pass-through options are both available. |
 |
Idling | Manual intervention was used to restore access to a historical copy of the relationship. |